Maslow's theory of motivation, also known as Maslow's hierarchy of needs, was proposed by psychologist Abraham Maslow in his 1943 paper "A Theory of Human Motivation".
Another name of this theory is humanistic theory, also known as Maslow's hierarchy of needs, theory ofpersonality; it is a motivational theory that describes the different levels of human needs that drive human behavior. Maslow believed that people are motivated to fulfill certain needs, and that these needs are organized in a hierarchy of five levels, with basic physiological and safety needs at the bottom and self-actualization needs at the top.
The five levels of Maslow's hierarchy of needs are:
1. Physiological Needs: This level includes basic needs such as food, water, shelter, and clothing. These needs must be satisfied before any other needs can be addressed.
2. Safety Needs: Once physiological needs are met, individuals seek safety and security. This includes physical safety, emotional safety, and financial security.
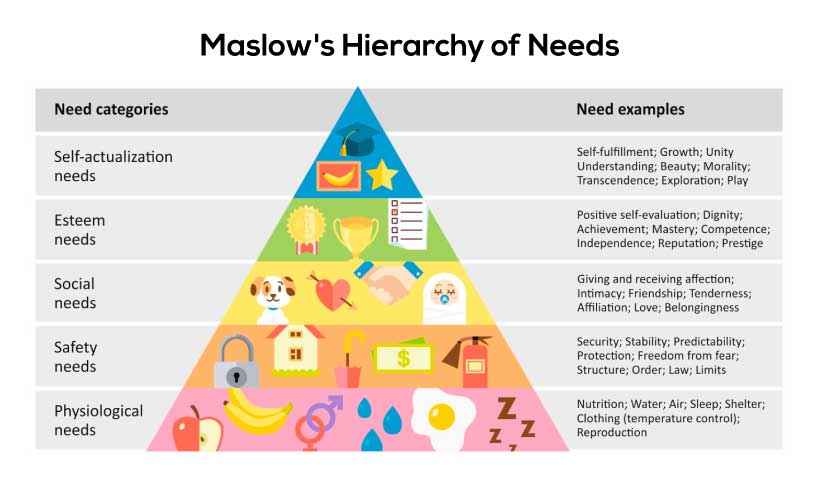
3. Love and Belonging Needs: This level includes the need for social connection and relationships. People seek love, friendship, and a sense of belonging to a group or community.
4. Esteem Needs: Once the previous needs are met, individuals seek to be respected and valued by others. This includes self-esteem and the need for recognition and achievement.
5. Self-Actualization Needs: This level involves the desire to reach one's full potential and achieve personal growth. It includes creativity, self-expression, and the desire to make a meaningful contribution to the world.
Maslow believed that people must satisfy their lower-level needs before they can focus on fulfilling higher-level needs. He also believed that individuals who reach self-actualization are characterized by creativity, spontaneity, and a strong sense of morality. Maslow's hierarchy of needs has been widely used in fields such as psychology, education, and management to understand and motivate human behavior.
Physiological needs of Maslow
Physiological needs refer to the most basic and fundamental biological requirements for human survival, including the need for air, water, food, shelter, and sleep. These needs are necessary for maintaining the body's homeostasis and ensuring its proper functioning.
Air is essential for breathing and the exchange of gases in the lungs, while water is crucial for maintaining hydration and regulating body temperature. Food provides the necessary nutrients and energy for the body to function, while shelter protects us from the elements and provides a safe and secure environment. Sleep is necessary for restoring and rejuvenating the body's cells and tissues, as well as for maintaining overall health and well-being.
Meeting physiological needs is the first and most fundamental step towards achieving higher levels of well-being and self-actualization. Without satisfying these basic needs, individuals cannot fully engage in other areas of life, such as social interactions, learning, creativity, and personal growth.
Safety needs of Maslow
Safety needs are a crucial component of Maslow's hierarchy of needs, which is a psychological theory that describes the five basic needs that motivate human behavior.
According to Maslow's hierarchy, safety needs are the second level of needs, which means that they must be fulfilled after physiological needs like food, water, and shelter are met. Safety needs refer to the need for security, stability, and protection from physical and emotional harm.
Examples of safety needs include having a safe and secure home, a stable source of income, access to healthcare, and protection from violence and danger. When these needs are not met, individuals may experience anxiety, fear, and a sense of insecurity, which can negatively impact their physical and mental well-being.
It's important to note that safety needs are not just limited to physical safety but also encompass emotional and psychological safety. For example, feeling emotionally safe in personal relationships and having a sense of belonging and acceptance can also be considered safety needs.
In summary, safety needs are a critical component of Maslow's hierarchy of needs, and when met, they allow individuals to feel secure and stable, both physically and emotionally, which is essential for their overall well-being.
Love and belonging needs of Maslow
Love and belonging needs are a crucial aspect of human development, according to Maslow's hierarchy of needs. These needs are social in nature and are considered to be the third level in the hierarchy, just above physiological and safety needs.
Love and belonging needs include the desire to form intimate relationships with others, to feel loved and cared for, and to have a sense of belonging and acceptance within a group or community. Examples of ways these needs can be met include forming close friendships, establishing romantic relationships, joining social clubs or organizations, and participating in family activities.
When love and belonging needs are not met, individuals may experience feelings of loneliness, social isolation, and depression. They may also have difficulty forming relationships with others or may engage in unhealthy behaviors to try and fill the void.
Meeting love and belonging needs is an essential part of human growth and development. Individuals who have these needs met tend to have better mental health outcomes and report higher levels of life satisfaction.
Esteem needs of Maslow
Esteem needs are one of the five categories of human needs in Maslow's hierarchy of needs. They refer to the desire for respect, recognition, and a positive sense of self-worth.
Maslow divided esteem needs into two types:
1. The first type is the need for self-esteem, which includes feelings of confidence, competence, and independence. This involves having a sense of achievement and self-respect, and feeling good about oneself.
2. The second type is the need for the esteem of others, which involves feeling valued, respected, and accepted by others. This includes receiving recognition, appreciation, and admiration from others.
Meeting esteem needs is important for individuals to feel good about themselves, be confident in their abilities, and develop a positive self-image. It can also lead to greater motivation, higher levels of achievement, and stronger relationships with others.
Maslow’s theory of self actualization
At the top of Maslow's hierarchy is self-actualization, which he defined as the process by which people achieve their full potential and become the best version of themselves.
Maslow believed that self-actualization is a natural and necessary goal for human beings, and that everyone has the potential to achieve it. However, he also recognized that many people never reach this level of development because they are too focused on meeting their more basic needs.
According to Maslow, self-actualization involves a number of characteristics, including creativity, spontaneity, acceptance of facts and reality, independence, a sense of humor, and a need for privacy. People who have achieved self-actualization are also likely to have strong interpersonal relationships, a sense of purpose in life, and a deep understanding of themselves and their place in the world.
Maslow's theory of self-actualization has been influential in many fields, including psychology, education, and business. It has been used to develop programs and interventions aimed at helping people achieve their full potential, and it continues to be a topic of research and discussion among psychologists and other scholars.
Maslow theory of motivation: advantages and criticism
Abraham Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory is a motivational theory that suggests that human needs are arranged in a hierarchical order, with physiological needs at the base, followed by safety, love/belonging, esteem, and self-actualization needs at the top. Here are some advantages and criticism of Maslow's theory:
Advantages:
1. Holistic approach: Maslow's theory takes a holistic approach to human motivation by considering a wide range of needs that people have, from basic physiological needs to self-actualization needs.
2. Hierarchical structure: The hierarchical structure of the theory is intuitive and easy to understand, providing a clear framework for understanding human motivation.
3. Real-life application: Maslow's theory has practical applications in areas such as management, education, and personal development.
4. Positive focus: Maslow's theory emphasizes the positive aspects of human motivation, such as self-actualization and personal growth.
Criticism of Maslow’s theory
Abraham Maslow's theory of hierarchy of needs is a well-known psychological framework that suggests that human beings have a set of innate needs that must be fulfilled in a certain order for individuals to achieve self-actualization, which is the highest level of personal growth and fulfillment. However, there have been several criticisms of Maslow's theory, including:
1. Cultural bias: Maslow's theory assumes that the hierarchy of needs is universal and applies to all cultures, but research has shown that cultural values and beliefs can significantly influence an individual's perception of needs and priorities.
2. Lack of empirical evidence: Maslow's theory is largely based on anecdotal evidence and case studies, and there is limited empirical research to support the theory.
3. Oversimplification: Maslow's theory suggests that needs must be met in a specific order, but in reality, individuals may prioritize needs differently depending on their circumstances and experiences.
4. Limited applicability: Maslow's theory is focused on individual motivation and does not account for external factors such as social and economic conditions that can impact an individual's ability to meet their needs.
5. Ignores individual differences: Maslow's theory assumes that all individuals have the same basic needs, but in reality, individuals may have unique needs and desires that are not accounted for in the hierarchy.
Overall, while Maslow's theory has been influential in the field of psychology, it has been subject to criticism for its oversimplification, lack of empirical evidence, and cultural bias.
Difference between Herzberg and Maslow theory
Herzberg's Two-Factor Theory and Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs Theory are two popular theories that are often used in the field of organizational behavior and management. Both theories attempt to explain what motivates individuals, but they differ in their approach and focus.
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs Theory proposes that people have five basic needs that must be satisfied in a specific order: physiological, safety, love/belonging, esteem, and self-actualization. Maslow believed that once a lower level of need is met, the individual will be motivated to fulfill the next higher level need. He suggested that individuals are motivated by the desire to reach self-actualization, which is the ultimate level of personal growth and fulfillment.
On the other hand, Herzberg's Two-Factor Theory suggests that there are two types of factors that motivate individuals: hygiene factors and motivators. Hygiene factors are the basic needs that must be met for an individual to feel comfortable at work, such as salary, job security, and working conditions. Motivators, on the other hand, are the factors that create job satisfaction and motivate individuals to perform at a higher level, such as recognition, achievement, and the work itself.
In summary, while both Herzberg and Maslow theories attempt to explain what motivates individuals, Maslow's theory focuses on individual needs and their hierarchy, whereas Herzberg's theory focuses on the workplace factors that lead to job satisfaction and motivation.
Conclusion:
Overall, while Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory has its limitations, it remains a useful framework for understanding human motivation and has had a significant impact on fields such as management and personal development.
Hierarchy of Needs Theory has laid the foundation for research, analysis, and explanation for people motivation. It has many limitations but it sparked the research and discussion of people motivation. Following this theory many other theories came mitigating its limitations. In this way people motivation has become a dominant area of Human Resource Management.








