International English Language Testing System (IELTS)
IELTS is an internationally recognized English Language Proficiency Certificate. Generally, IELTS helps people from countries whose mother tongue is not English to get visas for European and American countries. It is only for those who want to migrate or pursue higher study or work in a country where English is the native language. This testing procedure has been started since 1989.
IELTS is one of the two major tests to assess English proficiency. This test assesses the four main skills of a language. So today's concern is to let you know all about IELTS.
What is IELTS?
IELTS is an English language proficiency test. This test is the world's most popular test of English proficiency developed by a language center at the University of Cambridge. Globally this test can be taken by British Council and IDP. Locally many country wise organization administer this test. The questions are set by the Cambridge Assessment English Authority.
English is the third most spoken language in the world. More than 379 million people in the world speak English. So before applying for work, higher studies, or work in an English-spoken country IELTS is one of the best ways to test your proficiency in English.
Full Form of IELTS
IELTS is an abbreviation. The full form of IELTS is International English Language Testing System.
What is IELTS Exam/ IELTS Course
In the IELTS program, an examination is taken to assess the proficiency of English reading, writing, listening, and speaking of the candidates whose mother language is not English. In this examination, all of the candidates have to go through a test of four basic skills in the English language. These are:
1. Reading
2. Writing
3. Speaking
4. Listening
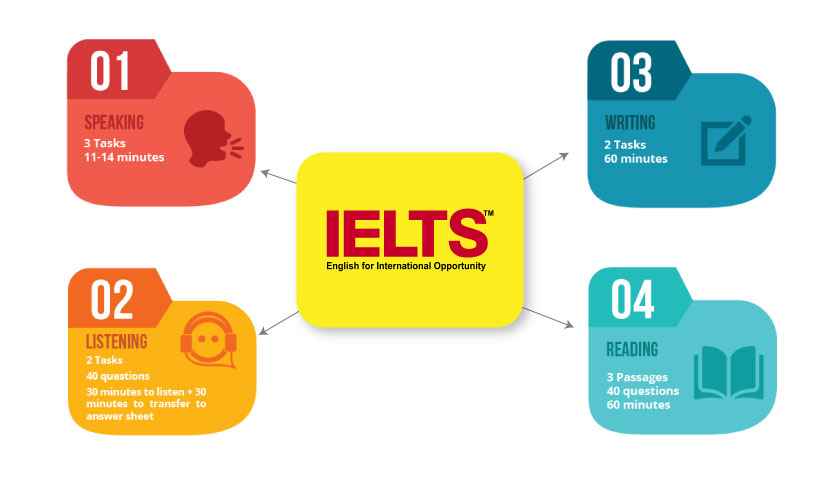
Candidates for IELTS have to sit for a four-part examination. The total time of the examination is more or less 3 hours. The individual timings of the examination are:
1. Reading: 40 questions/ 60 minutes
2. Writing: 2 tasks/ 60 minutes
3. Listening: 40 questions/ 40 minutes
4. Speaking : 3 parts/ 10-15 minutes
The test of reading, writing, and listening are held on the same day but the speaking test examination is sometimes taken on the same day or seven days before or after the other examinations.
The IELTS examination is held several times a year and the validity of the scorecard is for two years. Approximately 2 million candidates from more than 140 countries sit for the IELTS exam every year. There is more or less 1600 test center that exists all over the world.
IELTS Test Modules
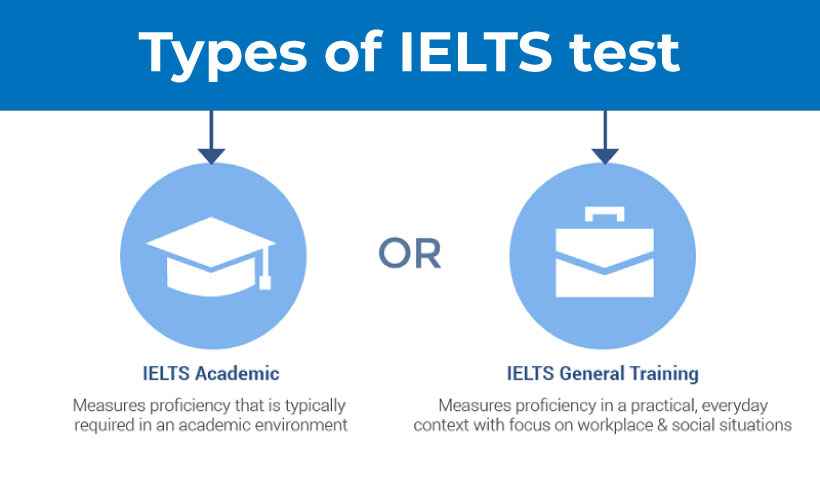
As we all know that IELTS is for testing the English reading, writing, listening, and speaking proficiency of non-natives by their birth. So if someone wants to go to a country whether for higher studies or migration, where English is their mother language then the applicants must sit for IELTS.
IELTS has two different test modules. The first is for those who want to go for higher studies called academic and the second is for those who want to migrate called general training. Speaking and listening test are the same for all the applicants of the two modules but the reading and writing tests are different.
Besides these two categories, there is one more module called IELTS Life Skill. IELTS Life Skills is meant for people who want to show their English speaking and listening competencies at the Common European Framework of Reference for Languages (CEFR) range A1 or B1. For those who applied for a family visa in the UK and need to improve their speaking and listening skills IELTS Life Skill is suitable for them.
IELTS Academic
IELTS Academic is for those who want to go for higher studies. This test assesses their ability to reading, writing, listening, and speaking as non-native. The test focuses on vocabulary which is one of the most essential parts of academic life. This test is also for understanding if the applicants are ready or not to study in English.
IELTS General
IELTS general is for those who want to go for a secondery degree or to migrate to a native English country, such as Australia, Canada, New Zealand, and the UK. In this category of the test, the proficiency of listening and speaking is being focused on.
As has been said earlier that four tests are taken in both of the modules of the IELTS exam. Speaking and reading test is the same but the reading and writing test are different from each other.
IELTS Writing Test
Writing tests for IELTS academic and IELTS general are different from each other. Both types of writing test formats are given below for your assistance.
• Academic Writing
The IELTS Academic writing test is combined with two tasks. They are, writing task 1 and writing task 2. All the candidates are asked to answer two tasks and both of the tasks must be answered.
In task 1 candidates have to explain or describe or summarize a piece of visual information in their own words. It takes 20 minutes and the word limit is 150.
In task 2 candidates have to respond to a point of view or argument or a problem in their own words. It takes 40 minutes and the word limit is 250.
Academic Writing Task 1
In academic writing task 1, a graph or a chart, or a diagram is given and the candidates are asked to describe the meaning or to summarize or explain the data presented on this visual presentation in their own words.
Writing task 1 takes 20 minutes. If anyone takes more than 20 minutes that means he/she lessens the allotted time for the second task.
The IELTS test takers have to write at least 150 words on task 1. Candidates can write more words if they can but they must be penalized if the answer is too short.
Candidates will be penalized for writing irrelevant topics. They must write their answers using full sentences. Candidates must not use any bullet points or their answers as notes. And they will be severely penalized if any plagiarism is checked by the authority of IELTS. The tone of the writing must be formal or semi-formal or neutral.
• What’s on Task 1
In task 1, one or more than one table, chart, or graph is given and the candidates are asked to describe or summarize it in their own words. And a diagram of a device or project or process is given and they have to explain the most important points of it. Here are some less important points that might be left.
• How to answer
You have to answer this task in at least 150 words within 20 minutes. You may write more words but not write less.
To properly complete your writing task you have to write:
1. an introduction
2. a summary of what you see or an overview of everything on the presented visuals
3. highlighting the key features or the main data
• What skills will be tested
What you understand and how you can describe or summarize or explain the thing presented on a visual by your understanding is the first thing to assess by task 1. Your proficiency to calculate the main point of the chart or table or diagram and how precisely and accurately you describe the main theme in an academic or formal tone without any grammatical mistake.
Academic Writing Task 2
In academic writing task 2, the candidates are given a subject to write down in an academic or semi-formal, or neutral style. Answers of the candidates need to be a discursive consideration of the relevant issues.
Academic writing task 2 appeared with a point of view, argument or problem. You might be asked to agree or disagree with a point of view, arguing on your point, and write about the negative and positive aspects of a topic or the reason for the problems and its preferred solution.
IELTS candidates are given 40 minutes to answer this task 2. They have to write at least 250 words. Again there is no penalty for long answers but you have to be penalized if the answer is too short or not relevant to the topic or if any kind of plagiarism is marked for the examiners. You should be penalized for not writing the whole text on a connecting note and using any kind of notes and bullet points.
The candidates must read the question paper carefully and write what it said to write. Candidates must write this task 2 in an essay format.
• What’s on Task 2
In Task 2, a problem or a point of view, or an argument is given and the candidates are requested to find a solution for this problem, justify their opinion, and explain the positive and negative sides of this solution.
• How to answer
First of all your response to this solution must be in an essay format. You must write your answers in the answer booklet. You must answer this task 2 in an academic or semi-formal or neutral style. You have to write at least 250 words in 40 minutes.
• What skills will be tasted
Task 2 assesses how you can write your ideas in a clear, relevant, and well-organized way. How perfectly you use your language to express your ideas and how precisely you can give your argument and can justify it in your way.
Task 2 assess your proficiency to:
1. Find a solution to a problem
2. Justify given opinion
3. Compare and contrast your opinion and implications
4. Examine and challenge proof or an argument.
General Training Writing
IELTS general training consists of two tasks, writing task 1 and writing task 2 and both of the tasks must be completed. The topics of the IELTS general training writing test are taken from general interest. The subjects may vary from household to space, illiteracy to the innovation of new ideas, etc.
In Writing Task 1, the candidates will be given a scenario in which they are asked to write down a letter to request information or provide an explanation for the given situation. Candidates have to write 150 words within 20 minutes to complete this task.
Writing Task 2 is a little bit different. The candidates are asked to write down an essay in reaction to some extent of view, argument, or problem. Candidates have to write 250 words within 40 minutes to complete this task.
Writing Task 1
Writing task 1 appeared with a situation and asked to write down an application or a letter to describe the public response in an informal, semi-formal, or formal style. The topics are of widespread interest.
Task 1 topics are from very common and familiar situations such as writing to the university authority to improve the facilities of the library or to the newspaper to enhance more recreational activities in an old home.
The allowed time for task 1 is 20 minutes and the word limit is 150 words. Anyone can write more than 150 words but the answers should not be less than the word limit.
The candidates must follow the rules of not using any bullet points and irrelevant topics otherwise he/she will be penalized.
• What’s on Task 1
In general training Task 1, the candidates are given a situation or topic from everyday life and they are asked to write down a response in 20 minutes. The word limit is 150. Candidates can write more but it is not allowed to write less.
The style of writing must be depended upon the situation given on the question paper. Candidates themselves choose the way of writing depending on the given situation is asked. Such as writing to an unknown is formal on the other hand writing to a known is personal or informal.
• How to answer
In task 1 the candidates are asked to list information in the form of bullet points. Candidates are required to explain a situation. To fulfill the requirements, the candidates have to do a number of the following: ask for and/or general information, specific needs, wants, likes or dislikes, particular complaints, make requests or make suggestions or recommendations.
• What skills will be tested
Examiners will examine the candidate's potential to use unique and appropriate use of vocabulary to provide facts about the concepts. This task also tests the candidate's ability to present their ideas, evidence, or argument as well as perspective and complaints concerning the tasks.
Writing Task 2
In writing task 2, the candidates are asked to write an essay on general interest. The assignment appeared with some information about a point of view or an argument or a problem. And the candidates are asked to discuss that information, provide more information, outline the problem or offer a solution, justify an opinion, comparing proof and ideas.
Task 2 contributes two times as a whole lot to the very last Writing band rating as Task 1. Therefore, taking a look at takers who fail to try to solve this venture will substantially lessen their hazard of accomplishing a very good rating.
IELTS candidates are given 40 minutes to answer this task 2. They have to write at least 250 words. Writing task 2 is almost double in comparison with writing task 1. So, if candidates fail to make a good score at writing task 2 then it can be easily said that he/she missed the chance a make a good score at all.
Again there is no penalty for long answers but you have to be penalized if the answer is too short or not relevant to the topic or if any kind of plagiarism is marked by the examiners.
• What’s on Task 2
In task 2 the candidates are asked to write an essay on general interest. They may be asked to write an essay on an argument, a problem, or a point of view.
• How to answer
Candidates should complete the task very carefully and make sure that all the response written is accurate, and relevant and that no grammatical mistakes have happened. They should sincerely organize their thoughts, and it may be from their personal experience. For this task, they need the ability to talk about complicated thoughts and have to use a wide range of vocabulary and grammatical structures.
• What skills will be tested
The examiner will assess how fluently or appropriately the information is provided. How properly the candidates use the given information, how to start and finish the discursive writing, how the candidates define a problem, give a solution, justify their opinion or compare and challenge ideas, proof or an argument is also been assessed.
Marking
Certificated IELTS examiners examine the candidates' overall performance on every writing test. There are 4 main criteria that the examiners assess when they give the mark of the candidates.
1. Task achievement for Task 1/Task response for Task 2
2. Coherence and cohesion
3. Lexical resource and
4. Grammatical range and accuracy.
Task achievement in task 1 and task reaction in task 2 assesses how accurately and relevantly your response covers the project requirements with the limitation of 150 words.
In Task 1, all of the facts you require are given in the diagram. In Task 2, Task reaction consists of how properly and perfectly you explain your argument in reaction to the mission, giving proof and examples which can be out of your personal experience.
Coherence and cohesion assess how clean and fluent your writing is, and how you organize thoughts and facts. It consists of giving your thoughts in a logical order, and the usage of several cohesive devices (for example, linking phrases, pronouns and conjunctions, etc.) correctly.
Lexical resource assesses your use of the variety and range of vocabulary and how properly and correctly you use it to explain your thoughts as well.
Grammatical range and accuracy assess the variety of grammar you've used and the way of using it appropriately and correctly.
IELTS Writing Tips
• Expand your vocabulary
Expanding your vocabulary level is the key to getting a good band score on IELTS writing tests. Because of the quality of your writing, and proper use of vocabulary, the style of your writing is tested through this test. Your ideas and thoughts are not tested, what is tested is how you express your thoughts and ideas.
• Keep your writing simple and clear
Always make sure that what you write is simple, clear, and easy to read and understand. It is unnecessary to make the sentence complicated by using difficult words.
• Avoid repetition
Repeating the same words over and over again makes a bad impression on the examiners. This habit of repetition shows low proficiency in your vocabulary level. Instead of repeating a word, use a synonym.
• Improve your grammatical accuracy
Grammatical accuracy is one of the most important tips to get a good band score on the IELTS writing test. Because
• Revise your writing
The allotted time for task 1 is 20 minutes and task 2 is 40 minutes. But this time is not enough to finish the whole task. But despite the lack of time, you must take at least 5 minutes at the end to review for any mistakes.
• Make full use of the exam period
Time management is very important in the IELTS writing test. An hour is not enough to complete the full task. In case you can't recognize the answer to one task, you just leave that and move on to the next one. And when this answer is complete then try to answer the left one. Another tip is that if you see the subject text is unknown to you, don’t be afraid. Look twice, the answer lies within the question.
• Try to understand the question
Before writing down the answer, understanding the question is one of the important tips for writing tests to get a good band score at IELTS.
• Check the spelling
Correct spelling is a must for obtaining a good band score. British, American, and Australian spelling is different from each other but all are equally accepted on the IELTS exam.
• Answer all questions
Answering all the questions on the question paper is one of the most important and effective tips for a good band score in IELTS writing. If any of the tasks are incomplete or not answered it reduces the chance to get a good score. So answering all the questions is a must.
• Maintain the standard structure
There are some structures to answer the tasks. And only by strictly following the structure, the candidates can achieve a good band score. Maintaining the standard structure is the tenth tip for a good band score in writing tasks.
Task 1 of the IELTS writing examination must be written as follows:
• Introduction: narrate what is in the graph.
• Overview: main state trends.
• Specific details: provide data and narrate particular changes.
The structures for task 2 are given below:
• Introduction: recheck the topic and convey your view.
• Body paragraph: each one must have a key idea that must be included in the first sentence.
• Conclusion: restate the presented opinion from the beginning.
• Do not write much
Writing much doesn't mean getting many scores. On the contrary, it leaves a boring impression on examiners. Besides this writing, much in task 1 can lessen the time for task 2.
• Keep the writing style the same
To get a good score on a writing test, the writing style must be the same. Mixing formal and informal tone puts a negative impact on getting a good score.
• Keep the writing style right
Except for general writing task 1, all the writing tasks should be written in a formal style. Only general module writing task 1 asked to write a letter in an informal style.
• Don’t write anything irrelevant
One thing should be remembered your writing must be relevant to the topic. This is one of the secret tips. And you should be penalized for irrelevant writing.
• Write only what you know about
Always write only what you know well. Never try to write what you don’t know well or know less. Your quality of English is tested through your answers. So you need an easy concept that you could truly describe and justify.
• Never memorize while preparing for writing a test
Never memorize model answers while you prepare yourself for the IELTS writing test. Because the percentage of getting the same essay you memorize is zero. So instead of memorizing spend more time on enhancing vocabulary level. And it will be beneficial for you to use numerous word phrases terms in different writings and show your huge variety of vocabulary.
IELTS Reading Test
Reading tests for IELTS academic and IELTS general are different from each other. Both types of reading test format details are given below for your assistance.
• Academic Reading
The Academic Reading test assesses a wide range of reading proficiency. This test is for evaluating your capability to follow and argument; realize a writer's mindset, opinion, and purpose. It tests appears how perfectly you can read and understand the main thoughts, details, opinions, and inherent meanings. Your reading comprehension talents are tested, including skimming, scanning, and reading for detail.
The academic reading test consists of 3 long texts. The text length is 2150-2750 words. These topics might be taken from contemporary books, journals, magazines, online resources, and newspapers. The texts are associated with topics you may face if you were to study at an undergraduate or postgraduate level or apply for professional registration in an English-speaking environment.
In an academic reading test, you have to answer 40 questions within 60 minutes (including transfer time). Each correct answer receives 1 mark. These questions are from a wide range, such as multiple choice, identifying information, short answer questions, identifying writer's views, labeling diagram, matching headings, completing a sentence, summary, note, table, and flow-chart completions.
• General Training Reading
In IELTS general training reading test, there are 3 sections. Section 1 is combined with two or three short texts. Or there may be several shorter texts. Section 2 consists of two texts and in section 3 there is one long text.
The text in section 1 is of regular topics. The types of texts that type of text which a person must understand while dwelling in an English-speaking country, such as notices, classified ads, and timetables.
Section 2 gives importance to work topics. For example, process descriptions, contracts, workforce improvement, and education materials. The text in section 3 appeared with a topic of general interest. The candidates have to write their statement in descriptive or instructive mode, as the question required.
Section 3 is longer and more complicated than section 1 and section 2. Section three texts are taken from newspapers, magazines, books, and online resources.
The academic reading test consists of 3 long texts. The text length is 2150-2750 words. In this test, you have to answer 40 questions within 60 minutes (including transfer time). Each correct answer receives 1 mark. These questions are of widespread types, such as multiple choice, identifying information, short answer questions, identifying writer's views, labeling diagram, matching headings, completing a sentence, summary, note, table, and flow-chart completions.
Types of questions
The question types of the IELTS reading test for academic and general training are the same. But there are differences between the topics. A detailed description of the questions types of the IELTS reading test is given below.
Question type 1 – Multiple choice
• What’s in it
This type of question is one kind of choosing the best answer. Here one question appeared with four or more possible answers. The candidates have to choose one or more required answers to fulfill the task as well.
This type of question may be the first part of a sentence and the candidates are asked to complete the sentence with the given possible answer.
The questions are in the same order as the information in the text: that is, the answer to the first question in this group will be located in the text before the answer to the second question, and so on. This task type may be used with any type of text.
• Number of questions
Variable
• What skills will be tested
This reading test assesses the talent of various kinds of reading skills. The candidate's ability to understand the main point of the topic or one specific point is tested through this test.
Question type 2 – Identifying information
• What’s in it
Candidates are given several statements and asked: 'Do the following statements agree with the information in the text?' They are then required to write 'true', 'false', or 'not given' in the boxes on their answer sheets.
It is very important to identify and understand the difference between 'false' and 'not given'. 'False' means that the passage states the opposite of the statement in question; 'not given' means that the statement is neither confirmed nor contradicted by the information in the passage.
Candidates must remember that they should not apply any statistics they know before whilst selecting their answers.
• Number of questions
Variable
• What skills will be tested
These types of questions assess the candidates’ capability to realize the specific points of the given text.
Question type 3 – identifying writer’s views/claims (Yes/No/Not given)
• What’s in it
Candidates are given several statements and asked: 'Do the following statement agree with the views or claims of the writer?' They were then required to write 'yes', 'no', and 'not given' in the boxes on their answer sheets.
• Number of questions
Variable
• What skills will be tested
These types of questions assess the candidates’ capability to realize the opinion or ideas and also the thoughts or mindset of the writer.
Question type 4 – Matching information
• What’s in it
In this part, candidates will be asked to find specific information in the paragraph or section of a text. The paragraphs are numbered by letters. And the candidates have to write the correct paragraph or sections in the boxes on their answer sheets.
Candidates are asked to find a specific detail, an example, a reason, a description, a comparison, a summary, an explanation, etc.
• Number of questions
Variable
• What skills will be tested
This task assesses the candidates' capability to quickly scan a text or paragraph to find specific information. Unlike task 5 (matching headings) this task focuses on specific information more than the main thought.
Question type 5 – Matching headings
• What’s in it
A list of headings identified with Roman lower cases (i, ii, iii, etc.) is given to the candidates. A heading conveys the main idea of the paragraph or section of a text. And the candidates are asked to match the correct paragraph or sections with the headings.
The paragraph or section of text is identified alphabetically (A, B, C, etc.). Candidates have to write the Roman numbers in the boxes of their answer sheets.
There will always be more headings than paragraphs or sections of the text so some headings will not be used. On the contrary, it is also possible that some paragraphs or sections may not be included in the task. A heading cannot be used twice.
• Number of questions
Variable
• What skills will be tested
Matching headlines tests the candidates’ capability of recognizing the main idea and how they differentiate between the main and supporting ideas.
Question type 6 – Matching features
• What’s in it
The candidates are required to match a set of statements or a piece of information to a list of options. The options are a set of functions from the text content. The lists of options are recognized through letters.
For example, the candidates are asked to match the name of the inventions with the inventors. It may be noticed that some options are not used and some will be used twice. If there are chances to use the option twice it will be mentioned on the question paper.
• Number of questions
Variable
• What skills will be tested
Matching features assesses the candidates' capability to understand relationships and connections among facts in the text and their ability to identify theories and opinions. The candidates have to be able to skim and scan the text to find the specific information easily and quickly to read the text for detail.
Question type 7 – Matching sentence endings
• What’s in it
The candidates are given a list of the first half of a sentence and are asked to match the sentence endings from another list of the possible answer endings. The answers to the ending sentences are identified by alphabetical numbers and the candidates have to write down the numbers on their answer sheet.
There will be more ending sentences than beginning sentences. So the candidates should choose carefully the right one. The sentence beginnings are in the same order as the information in the text.
• Number of questions
Variable
• What skills will be tested
Matching sentence endings assesses the candidates’ ability to understand the main thoughts and ideas of the text.
Question type 8 – Sentence completion
• What’s in it
The candidates are asked to fill in the gap in each sentence from the words of the text. They have to write the right words on the answer sheet.
The required number of words to complete the sentence is mentioned in the question and the candidates must follow this strictly. For example, 'One Word Only', and 'No More Than Two Words/Numbers'.
Contracted words, such as “you’ve” will not be tested. Hyphenated words, such as “short-term”, count as single words.
• Number of questions
Variable
• What skills will be tested
This task assesses the candidates' ability to find particular information from a detailed text or a section of a text.
Question type 9 – Summary, note, table, flow-chart completion
• What’s in it
The candidates are given a precise segment of the text and are required to complete it with data or information from the text. The given data can be in the form of various connected sentences of a text which is called a summary, various notes which are called notes, a table with one or more empty cells which is called a table, a series of steps or boxes connected with arrows to show a sequence of events but some of the boxes are empty which called flow-chart.
There are two versions of this task. One in which the candidates are asked to choose from answers from the text and the other in which they have to choose from a list of answers.
The required number of words to complete the sentence is mentioned in the question and the candidates must follow this strictly. For example, 'One Word Only', and 'No More Than Two Words/Numbers'.
Contracted words, such as “you’ve” will not be tested. Hyphenated words, such as “short-term”, count as single words.
• Number of questions
Variable
• What skills will be tested
This task assesses the candidates' ability to find particular information from a detailed text or a section of a text. When completing the sentence the candidates have to be careful about the right form of the word to fill in the gaps, such as whether an adjective or adverb or a noun is needed.
Question type 10 – Diagram label completion
• What’s in it
The candidates are asked to complete the label of a diagram. The diagram may be of some type of machine or may be of a building or any kind of element shown in the picture.
The required number of words to complete the sentence is mentioned in the question and the candidates must follow this strictly. For example, 'One Word Only', and 'No More Than Two Words/Numbers'.
Contracted words, such as “you’ve” will not be tested. Hyphenated words, such as “short-term”, count as single words.
• Number of questions
Variable
• What skills will be tested
The candidates’ ability to understand the detailed description and how they relate that description to data given in a diagram is assessed by this task.
Question type 11 – Short answer questions
• What’s in it
The candidates have to answer questions about factual details in the text. They have to write answers in words or numbers on the answer sheet.
The required number of words to complete the sentence is mentioned in the question and the candidates must follow this strictly. For example, 'One Word Only', and 'No More Than Two Words/Numbers'.
Contracted words, such as “you’ve” will not be tested. Hyphenated words, such as “short-term”, count as single words.
• Number of questions
Variable
• What skills will be tested
This test assesses the candidates’ ability to recognize
and realize the particular data in the text.
Marking
An experienced team of certified markers marked the IELTS reading test. The markers are monitored to ensure reliability. The answer sheets are analyzed twice. First, it is analyzed by the certified markers and second by the team of Cambridge English.
IELTS Reading Tips
i. Skimming
Skimming is reading rapidly to get an overall view of the text. In the reading test, there is no additional time for detail and relaxed reading. So you have to skim over the text to get a general overview of the text.
ii. Scanning
Scanning is reading rapidly to find the particular text. The text may include important dates, numbers, times, and names. When scanning underline the important features and it will help you to answer questions quickly. You do not get additional time so you should be fast, focused, and alert.
iii. Underline
When you read the text, underline the important words, and lines. It will help to find the right answer quickly.
iv. Answer all questions
It is a great suggestion for getting a good band score that all the questions should be answered. If you are not sure of the right answer, try your luck and write the answer you think is right. There is no minus marking for the wrong answer.
v. Avoid facts that you already know about the topic
Candidates often do this mistake. They make an assumption based on their knowledge. Always try to base your answer on the text only. Avoid the facts you already know about the topic.
vi. Time management
Managing time is very important in the IELTS reading test. The candidates have to read 3 texts and answer 40 questions within 60 minutes (including transfer time). And there is no rule for additional time.
vii. Read the instruction carefully
When answering always read the instruction carefully. Follow the instructions that are mentioned in the questions. For example, if the instruction requires ‘two words’ and the answer is black and white, the candidates must write, ‘black, white’ not ‘black and white’. ‘Black and white’ are three words and therefore incorrect.
Again, if it requires 'one word', it means only one word. If the text says 'an elephant' but the question asked for 'one word only' the candidates should write 'elephant'. 'An elephant' is two words and therefore wrong.
viii. Don't be afraid of the unknown words
Commonly, some questions are easy and some are difficult. So when you see some unknown and unfamiliar words, it's a great tip that doesn't be afraid or panicked. Every answer is in the text, you just read carefully and find the answer.
ix. The idea should be focused
In the IELTS reading test, the only focus matter is the ideas or thoughts, not the words. How the candidates recognize the thoughts of the main text and how they describe this in their own words are the main concept.
x. Correct spelling is mandatory
Writing answer with correct spelling is mandatory in the IELTS reading test. You will get no marks for a misspelled word when the answer is right.
xi. The order should be the same
Always try to keep the order the same. It should be remembered that the question follows the order of the text. And that is why the answer to question 4 ultimately comes after the answer to question 3 and so on.
xii. Improve reading skill
Improving reading skills is one of the most important tips for getting a good band score on the IELTS reading test. Reading for the exam is boring and monotonous but reading for entertainment is a pleasure. Reading a little every day is a pleasure and it will improve your reading skill as well as increase your vocabulary level.
IELTS Listening Test
The IELTS listening test is the same for both IELTS academic and IELTS general training.
The IELTS listening test is a combination of four different types of recordings of native speakers. Every four parts appeared with ten questions. The questions are in the same order in which the recording is played.
Part 1 and Part 2 are set from everyday social concepts.
Part 1 is a conversation between two native speakers who are speaking about an everyday topic. The topic may be a conversation about the arrangement of a picnic or any kind of topic that sets in daily life concepts.
Part 2 is a monologue or one-person speech on the topic of local facilities.
Part 3 and Part 4 are set from the topics of education and training.
Part 3 is a conversation between two speakers. It may be a discussion
between two university students, perhaps guided by a tutor.
Part 4 is again a monologue or one-person speech on any kind of academic topic.
The recordings are heard only once. And these recordings include different accents, British, American, New Zealand, North American, Canadian, and Australian accents are used.
The candidates have to answer 40 questions within 30 minutes (additional 10 minutes to transfer). Each correct answer receives 1 mark and there is no negative marking for wrong answers.
Types of Questions
There are a variety of questions are used to assess the candidates' ability to understand different types of conversation in different accents. A detailed description of different types of questions is given below for your assistance.
Question type 1 – Multiple choice
• What’s in it
This type of question is one kind of choosing the best answer. Here one question appeared with four or more possible answers. The candidates have to choose one or more required answers to fulfill the task as well.
This type of question may be the first part of a sentence and the candidates are asked to complete the sentence with the given possible answer.
The questions are in the same order as the information in the text: that is, the answer to the first question in this group will be located in the text before the answer to the second question, and so on.
• Number of questions
Variable
• What skills will be tested
This task assesses the candidates' proficiency in listening skills. The candidate's understanding of the main points or the particular point of the recording is the main focus of this task.
Question type 2 – Matching
• What’s in it
In this part, the candidates are given a list of items from the recording and they are asked to match this with a list of options.
• Number of questions
Variable
• What skills will be tested
The candidates’ capability of following a conversation of two or more people is being judged. It assesses the proficiency of listening for detailed information from a conversation on an everyday topic. This test also tests the candidates' skills to understand the relationships and connecting facts in the recordings.
Question type 3 – Plan, map, diagram labeling
• What’s in it
In this section, the candidates are asked to complete a label on a visual. It may be a plan of a building or a map of a city or a diagram of a piece of equipment.
The candidates have to pick the right answer from the list mentioned on the question paper. The candidates have to use the same words told in the recording and no matter what the word can't be changed.
Again the word limit must be followed mandatory and the answer counted as wrong if the word limit is violated.
• Number of questions
Variable
• What skills will be tested
This test assesses the capability to understand, for example, an outline of a place, and how the candidates connect this to a visual presentation. This may also assess the candidates’ skill to recognize the direction properly.
Question type 4 - Form, note, table, flow-chart, summary completion
• What’s in it
In this task, the candidates are asked to fill in the blanks in an outline of part or of the whole recording text. The test focuses on the chief ideas of the text. It might be:
a form: used to record facts, such as names
or a set of notes: used to summarize information and show how different items relate to one another
a table: is used to summarize information that relates to clear categories, for example, place, time, and price.
a flow chart: is used to summarize the stages in a process, with the direction of the process shown by arrows.
The candidates have to pick up the right answer from a list on the question paper. They may also have to find the missing words from the recordings.
The candidates have to use the same words told in the recording and no matter what the word can't be changed.
Again the word limit must be followed mandatory and the answer counted as wrong if the word limit is violated.
• Number of questions
Variable
• What skills will be tested
This task focuses on key points that a listener would naturally record in this type of situation.
Question type 5 – Sentence Completion
• What’s in it
The candidates are required to read a set of sentences and summarize key information from one part of the whole recording. And then the candidates have to fill in the gap in each sentence using the information from the recordings.
The candidates have to use the same words told in the recording and no matter what the word can't be changed.
Again the word limit must be followed mandatory and the answer counted as wrong if the word limit is violated.
• Number of questions
Variable
• What skills will be tested
These types of questions focus on the candidates’ ability to recognize important information in a recording. The candidates have to understand relationships between ideas/facts/events, such as cause and effect.
Question type 6 – Short answer question
• What’s in it
In this section, the candidates have to read a question and then answer them with the information from the recordings.
The required number of words to complete the sentence is mentioned in the question and the candidates must follow this strictly. For example, 'One Word Only', and 'No More Than Two Words/Numbers'.
Contracted words, such as “you’ve” will not be tested. Hyphenated words, such as “short-term”, count as single words.
In many cases, the candidates are asked to write several answers to one question.
• Number of questions
Variable
• What skills will be tested
Short answer question assesses the candidates’ ability to understand the facts told in the recordings. It may be price, place, time, and so on.
Marking
An experienced team of certified markers marked the IELTS reading test. The markers are monitored to ensure reliability. The answer sheets are analyzed twice. First, it is analyzed by the certified markers and second by the team of Cambridge English.
IELTS Listening Tips
• Improve your listening skill
Improving listening skills is one of the most important ways to get a good band score on the IELTS listening test. You may watch tv shows and movies but watching various shows like, Ted talks, news reports, documental programs, and podcasts make you familiar with different accents and a new range of vocabulary.
• Try to catch the keyword
When listening to the audio, try to catch the keywords. Questions will be given before playing the recording. When you read the question try to understand the keyword and underline it. Pay attention and guess the right forms of words, and what is needed.
• Write the answers carefully
Write the answers very carefully when transferring them to the answer sheet. Be careful with capitalization. If you are unsure about this, write all in capital letters.
• Concentrate on the audio
Pay deep attention when the audio is playing. Try to concentrate on what the audio saying because all the questions and answers are on the audio.
• Try to be familiar with different accents
It is a very important tip to get a good band score on the IELTS listening test that you must try to be familiar with different types of accents. Not all places or countries have the same accents. So you should be familiar with different types of accents.
• Follow the instruction carefully
When answering always read the instruction carefully. Follow the instructions that are mentioned in the questions. For example, if the instruction requires ‘two words’ and the answer is black and white, the candidates must write, ‘black, white’ not ‘black and white’. ‘Black and white’ are three words and therefore incorrect.
Again, if it requires 'one word', it means only one word. If the text says 'an elephant' but the question asked for 'one word only' the candidates should write 'elephant'. 'An elephant' is two words and therefore wrong.
• Don’t try to answer too quickly
Don't try to answer too quickly because the sentence you hear first proves wrong in the second sentence. So don't make a hurry to answer. Take your time to hear the full recording and then answer your questions.
• Answer all questions
It is a great suggestion for getting a good band score that all the questions should be answered. If you are not sure of the right answer, try your luck and write the answer you think is right. There is no minus marking for the wrong answer.
• Check the spelling
Writing answer with correct spelling is mandatory in the IELTS reading test. You will get no marks for a misspelled word when the answer is right.
• Try to guess the answer
When listening to the recording try to guess the answer. Sometimes it proves wrong but most of the time it will save you time.
• Focus on ‘what’, not ‘how’
Always focus on 'what' the audio says, not 'how' the audio says. Because you will find answers in what is said, not how it is said.
IELTS Speaking Test
The IELTS speaking test is one kind of face-to-face conversation between the candidate and the examiner. Each part is different from the others and every part follows a particular pattern of tasks to test the candidates' ability to speak in different situations and ways.
The IELTS speaking test is a combination of 3 parts. Each part lasts for approximately 4-5 minutes. The total time of the test is about 11-14 minutes.
Part 1 is a discussion of general questions. The examiner will ask questions about the candidates' self and a wide range of the candidates' familiar topics. Part 1 takes 4-5 minutes to complete.
Part 2 is about a specific topic. The candidates have to answer orally one or two questions on this particular topic. It takes 4-5 minutes to complete.
Part 3 is a detailed discussion on the topic of Part 2. The examiner will ask further questions on this topic. It takes 4-5 minutes to complete.
Every part of the speaking test is recorded.
Types of questions
The detailed question patterns of the IELTS speaking test are given below for your assistance.
Part 1 – Introduction and Interview
• What’s in it
In this part, the examiner introduces him/her and checks the candidates' identities. After this, the examiner asked questions about some familiar topics. The topics may be the candidates' home, family, hobby, interest, work, aim, internet, etc.
Part 1 is 4-5 minutes long.
• Number of questions
Variable
• What skills will be tested
This test checks the candidates' capability to provide information and opinions on everyday familiar topics and share common experiences by answering several questions.
Part 2 – Long Run
• What’s in it
Part 2 is the individual long run. The examiner gives a task card to the candidate and asked the candidate to talk on this specific topic. The task card includes some points and what the candidate do is cover all the points mentioned on the task card.
The candidates' have to explain at least one aspect of this topic. The candidates are given 1 minute to prepare his/her speech. A pencil is given to take notes.
The examiner asked the candidate to talk for 1-2 minutes and then stop after 2 minutes. The examiner then asked 1 or 2 questions on this topic.
Part 2 lasts for 4-5 minutes, including the preparation time.
• Number of questions
Variable
• What skills will be tested
The candidates' capability of speaking on a given topic for a certain period and how they use language to establish their thoughts is the main issue of this task.
Part 3 – Discussion
• What’s in it
Part 3 is another discussion between the examiner and the candidates on the same topic as part 2 but in a more detailed and abstract way.
Part 3 lasts 4-5 minutes.
• Number of questions
Variable
• What skills will be tested
The candidates’ ability to explain their established opinions is the main thing to test through this test. How the candidate analyzes and speculates about issues is also tested by this task.
Marking
The IELTS speaking test assesses the candidates' speaking skills in any situation and any topic. There are 4 factors on which a good band score depends. They are:
• Fluency and coherence
• Lexical resource
• Grammatical range and accuracy
• Pronunciation.
Fluency and coherence assess your speaking proficiency at normal speed. It tests how nicely the candidates communicate without any hesitation. It includes putting sentences and thoughts in a logical order and the use of cohesive devices (such as linking words, pronouns and conjunctions, etc.) correctly so that what you assert isn't always tough to follow.
Lexical resource assesses the candidates’ use of a variety of vocabulary and how properly they use it to express their meaning. It tests the candidates' ability to use the alternative word when he/she doesn't know a specific word.
Grammatical range and accuracy assess the candidates' capability of using a variety of grammar and how appropriately and accurately they operate this while speaking.
Pronunciation assesses the candidates’ proficiency to talk in a manner that may be understood without excessive effort.
IELTS Speaking Tips
Some tips to get a good band score on the IELTS speaking test are mentioned below.
• Practice
Practice makes a man perfect. Try to practice speaking a little bit every day. This will gradually improve your speaking skill.
• Expand your vocabulary
Expanding vocabulary is one of the most important tips to get a good band score not only the speaking but all four exams in the IELTS program.
• Be fluent
It is more important to be fluent than to use uncommon vocabulary. Only fluent and spontaneous speakers gain more points.
• Ask the question twice if you don’t understand
If you don't understand the question, do not hesitate to ask the examiner twice. Make an apology and ask the question twice, as simple as that.
• Try to extend your answer
Always try to give your answer in a detailed way. Suppose, the examiner asks you a question and you can answer it in one or two words. Never do this. Always give your answer in full sentences.
• Be coherent
Using linking words and structures will make your speech rich. Use, however, nevertheless, all in all, moreover, etc. in your speech.
• Take time to think
Do not hurry when answering a question. Listen carefully, try to understand the question, and then take a moment to prepare the answer. Take a little bit of time to think before delivering your answer. But don't waste too much time, because the test has a time limit.
• Correct your mistakes
It is very common to make a silly mistake when communicating in a foreign language. So when you made a mistake don't be panicked, make an apology and repeat the sentence correctly. It will let your examiner know that you do know your grammar and vocabulary.
• Don’t think about accent
It is not necessary that you must speak in the accents of a native speaker. So don't be panicked over accents.
• Emphasize on pronunciation
Always try to speak with the correct pronunciation. If the examiner doesn't understand what you said because of your poor pronunciation, surely you will lose your mark.
IELTS Score
There is no pass or fail in the IELTS exam. The result of this examination is scored on a band scale. The range of the band score is between 0-9.
The 9-band scale is described as follows:
|
Band |
User type |
Description |
|
9 |
Expert User |
Has fully operational command of the language: appropriate, accurate, and fluent with complete understanding. |
|
8 |
Very good user |
Has fully operational command of the language with only occasional unsystematic inaccuracies and inappropriateness. Misunderstandings may occur in unfamiliar situations. Handles complex detailed argumentation well. |
|
7 |
Good user |
Has operational command of the language, though with occasional inaccuracies, and misunderstandings in some situations. Generally handles complex language well and understands detailed reasoning. |
|
6 |
Competent user |
Has generally effective command of the language despite some inaccuracies, and misunderstandings. Can use and understand fairly complex language, particularly in familiar situations. |
|
5 |
Modest user |
Has partial command of the language, coping with overall meaning in most situations, though is likely to make many mistakes. Should be able to handle basic communication in own field. |
|
4 |
Limited user |
Basic competence is limited to familiar situations. Has frequent problems with understanding and expression. Is not able to use complex language. |
|
3 |
Extremely limited user |
Conveys and understands only general meaning in very familiar situations. Frequent breakdowns in communication occur. |
|
2 |
Intermittent user |
No real communication is possible except for the most basic information using isolated words or short formulae in familiar situations and to meet immediate needs. Has great difficulty understanding spoken and written English. |
|
1 |
Not user |
Candidates cannot use the language except a few words |
|
0 |
Did not attempt the test |
Candidates did not answer the questions which are provided |
IELTS Exam Fees
Unfortunately, there are no fixed fees for the IELTS examination. Because many IELTS examination fees depend on the test center and the country where the IELTS exams are taken. But the approximate fees for the IELTS exams can vary from $140-$310.
In some cases, the IELTS test centers charge a flat fee of $225, but this is subject to change. And make sure to search for information about the exam fees and other related details about the nearest testing center in advance.
IELTS Exam Service Provider
IELTS is jointly owned by the British Council, IDP: IELTS Australia, and Cambridge English. And these organizations provide the IELTS exam through 1600 testing centers in 140 countries of the world.
So, that’s all for today. Hope you can find all your queries about the IELTS exam from this above writing. Goodbye for now. Stay well with knowledge.
There are thousands of IELTS Prep support centre all over the world. In Bangladesh there are many service providers for IELTS preparation.








